The Kossiakoff Group’s research interests are to provide a molecular understanding of how molecular recognition governs virtually all aspects of biological function. To study these issues our group employs a combination of X-ray crystallography and cryo-EM, site-directed mutagenesis, phage display and biophysical analysis. The Kossiakoff group has also pioneered a new technology called “chaperone-assisted” crystallography, which has facilitated the structural analyses of protein systems that had been totally recalcitrant to other approaches. The group has also been at the forefront of developing synthetic antibodies. These synthetic antibodies are much more powerful than traditional monoclonal antibodies and have the potential to completely replace them for uses in live cell imaging and proteomics.
Latest Publications
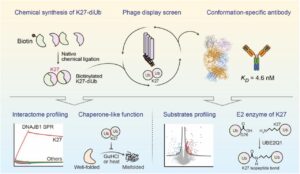
Han C; Weng Y; Zheng Q; Qu Q; Erramilli S K; Su Z; Duan Y; Han Y; Zhai X; Li J; Kossiakoff A A; Pan M; Zhao M; Liu L; Yu Y
Conformation-specific Antibody Deciphers K27-linked Ubiquitination in Chaperone-Mediated Proteostasis Journal Article
In: bioRxiv, 2025, ISSN: 2692-8205.
@article{pmid41446272,
title = {Conformation-specific Antibody Deciphers K27-linked Ubiquitination in Chaperone-Mediated Proteostasis},
author = {Chengxiao Han and Yicheng Weng and Qingyun Zheng and Qian Qu and Satchal K Erramilli and Zhen Su and Yujuan Duan and Yunxi Han and Xiaoguo Zhai and Jingxian Li and Anthony A Kossiakoff and Man Pan and Minglei Zhao and Lei Liu and Yuanyuan Yu},
doi = {10.64898/2025.12.18.695067},
issn = {2692-8205},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-12-01},
urldate = {2025-12-01},
journal = {bioRxiv},
abstract = {Lysine 27 (K27)-linked polyubiquitination plays critical yet incompletely defined roles in proteostasis, innate immunity, and disease progression; however, investigations into this process have long been hindered by its extremely low abundance and the lack of conformation-specific enrichment tools. Herein, we describe the development of a long-sought conformation-specific antibody, K27-IgG, which can selectively recognize-among all ubiquitin chain types-the unique architecture of K27-linked polyubiquitin (K27-polyUb) characterized by a distinct buried K27-isopeptide bond, with high affinity (KD = 4.66 nM). This antibody was derived from synthetic antibodies initially generated via phage display, using chemically synthesized K27-linked diubiquitin (K27-diUb) as the antigen. High-resolution co-crystal structures uncovered the unique K27-diUb interface targeted by these sAbs. Subsequent reformatting of these sAbs into a full-length human immunoglobulin G (IgG) scaffold yielded K27-IgG, notably exhibiting markedly enhanced affinity without compromising selectivity. Using K27-IgG as a tool, we achieved sensitive detection and immunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous K27-polyUb in cells, and delineated the intracellular interaction landscape of K27-polyUb through complementary proteomic approaches. Two key findings emerged: 1) The molecular chaperone DNAJB1 is a specific reader of K27-linked ubiquitin chains (but not other linkages) and that K27-polyUb chains themselves exhibit chaperone-like activity, suggesting a novel mechanism by which K27-polyUb regulates chaperone-mediated proteostasis; 2) The E2 enzyme UBE2Q1 assembles K27-diUb, identifying it as a potential writer for this ubiquitin chain topology. Collectively, this study establishes K27-IgG as a robust tool for deciphering the K27-linked ubiquitin code, thereby opening new avenues for investigating the biological functions of K27-linked polyubiquitination.nnHIGHLIGHTS: First K27-linkage conformation-specific antibody with nanomolar affinity overcomes a major barrier in the field.K27-IgG unlocks functional mapping of the K27 ubiquitin landscape under proteotoxic stress.Molecular chaperone DNAJB1 is a selective "reader" of K27-linked ubiquitin chains.K27 chains possess intrinsic chaperone activity, enabling protein refolding and suppressing aggregation.E2 enzyme UBE2Q1 is a "writer" that directly assembles K27-linked ubiquitin chains.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
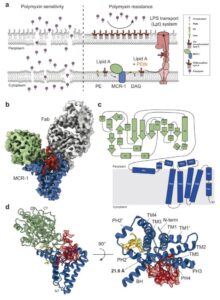
Zinkle A P; Batista M B; Herrera C M; Erramilli S K; Kloss B; Ashraf K U; Nosol K; Zhang G; Cater R J; Marty M T; Kossiakoff A A; Trent M S; Nygaard R; Stansfeld P J; Mancia F
Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial resistance mediated by the phosphoethanolamine transferase MCR-1 Journal Article
In: Nat Commun, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 10516, 2025, ISSN: 2041-1723.
@article{pmid41298376,
title = {Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial resistance mediated by the phosphoethanolamine transferase MCR-1},
author = {Allen P Zinkle and Mariana Bunoro Batista and Carmen M Herrera and Satchal K Erramilli and Brian Kloss and Khuram U Ashraf and Kamil Nosol and Guozhi Zhang and Rosemary J Cater and Michael T Marty and Anthony A Kossiakoff and M Stephen Trent and Rie Nygaard and Phillip J Stansfeld and Filippo Mancia},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-025-65515-3},
issn = {2041-1723},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-01},
urldate = {2025-11-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {16},
number = {1},
pages = {10516},
abstract = {Polymyxins are used to treat infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. They are cationic peptides that target the negatively charged lipid A component of lipopolysaccharides, disrupting the outer membrane and lysing the cell. Polymyxin resistance is conferred by inner-membrane enzymes, such as phosphoethanolamine transferases, which add positively charged phosphoethanolamine to lipid A. Here, we present the structure of MCR-1, a plasmid-encoded phosphoethanolamine transferase, in its liganded form. The phosphatidylethanolamine donor substrate is bound near the active site in the periplasmic domain, and lipid A is bound over 20 Å away, within the transmembrane region. Integrating structural, biochemical, and drug-resistance data with computational analyses, we propose a two-state model in which the periplasmic domain rotates to bring the active site to lipid A, near the preferential phosphate modification site for MCR-1. This enzymatic mechanism may be generally applicable to other phosphoform transferases with large, globular soluble domains.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
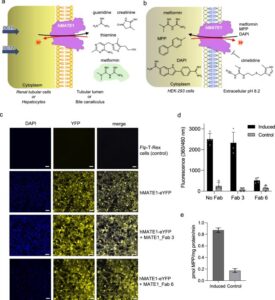
Romane K; Peteani G; Mukherjee S; Kowal J; Rossi L; Hou J; Kossiakoff A A; Lemmin T; Locher K P
Structural basis of drug recognition by human MATE1 transporter Journal Article
In: Nat Commun, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 9444, 2025, ISSN: 2041-1723.
@article{pmid41145429,
title = {Structural basis of drug recognition by human MATE1 transporter},
author = {Ksenija Romane and Giulia Peteani and Somnath Mukherjee and Julia Kowal and Lorenzo Rossi and Jingkai Hou and Anthony A Kossiakoff and Thomas Lemmin and Kaspar P Locher},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-025-64490-z},
issn = {2041-1723},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-28},
urldate = {2025-10-01},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {16},
number = {1},
pages = {9444},
abstract = {Human MATE1 (multidrug and toxin extrusion protein 1) is highly expressed in the kidney and liver, where it mediates the final step in the excretion of a broad range of cationic drugs, including the antidiabetic drug metformin, into the urine and bile. This transport process is essential for drug clearance and also affects therapeutic efficacy. To understand the molecular basis of drug recognition by hMATE1, we determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of the transporter in complex with the substrates 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP) and metformin and with the inhibitor cimetidine. The structures reveal a shared binding site located in a negatively charged pocket in the C-lobe of the protein. We functionally validated key interactions using radioactivity-based cellular uptake assays using hMATE1 mutants. Molecular dynamics simulations provide insights into the different binding modes and dynamic behaviour of the ligands within the pocket. Collectively, these findings define the structural basis of hMATE1 substrate specificity and shed light on its role in drug transport and drug-drug interactions.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
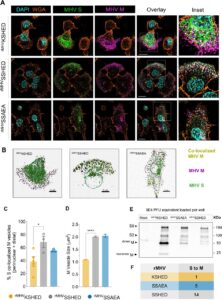
Mohona S; Shakya A K; Singh S; Kearns F L; Jemison K; Erramilli S; Dey D; Qing E; Jennings B C; Doray B; Kossiakoff A A; Amaro R E; Klose T; Gallagher T; Hasan S S
An unconventional HxD motif orchestrates coatomer-dependent coronavirus morphogenesis Journal Article
In: bioRxiv, 2025, ISSN: 2692-8205.
@article{pmid41279991,
title = {An unconventional HxD motif orchestrates coatomer-dependent coronavirus morphogenesis},
author = {Surovi Mohona and Anil K Shakya and Suruchi Singh and Fiona L Kearns and Kezia Jemison and Satchal Erramilli and Debajit Dey and Enya Qing and Benjamin C Jennings and Balraj Doray and Anthony A Kossiakoff and Rommie E Amaro and Thomas Klose and Tom Gallagher and S Saif Hasan},
doi = {10.1101/2025.10.16.682669},
issn = {2692-8205},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-17},
urldate = {2025-10-01},
journal = {bioRxiv},
abstract = {Assembly of infectious coronaviruses requires spike (S) protein trafficking by host coatomer, typically via a dibasic signal in the S cytoplasmic tail. However, the human embecoviruses HKU1 and OC43, as well as the model virus MHV, lack this motif. Here we identify a conserved His-x-Asp (HxD) sequence that functions as an unconventional coatomer-binding signal. Structural and biochemical analyses show that the MHV HxD motif engages coatomer subunits through distinct conformations, while cellular imaging demonstrates its role in directing S to assembly sites with the viral M-protein. Disruption of HxD-coatomer interactions impairs S incorporation and provokes compensatory viral adaptations, including emergence of a canonical dibasic motif or mutations in M-protein. Electron microscopy further reveals profound alterations in virion surface architecture. These findings uncover HxD as a previously unrecognized coatomer-targeting motif, highlighting an unexpected flexibility in coronavirus assembly pathways and broadening understanding of the cellular machinery that shapes coronavirus morphogenesis.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
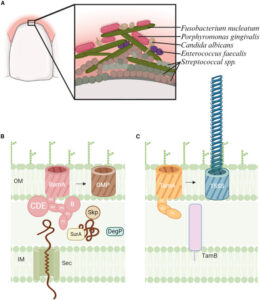
Cottom C O; Heinz E; Erramilli S; Kossiakoff A; Slade D J; Noinaj N
Characterization of the OMP biogenesis machinery in Fusobacterium nucleatum Journal Article
In: Structure, vol. 33, iss. 33, no. 11, pp. 1878–1892.e5, 2025, ISSN: 1878-4186.
@article{pmid40897170,
title = {Characterization of the OMP biogenesis machinery in Fusobacterium nucleatum},
author = {Claire Overly Cottom and Eva Heinz and Satchal Erramilli and Anthony Kossiakoff and Daniel J Slade and Nicholas Noinaj},
doi = {10.1016/j.str.2025.08.008},
issn = {1878-4186},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-09-01},
urldate = {2025-09-01},
journal = {Structure},
volume = {33},
number = {11},
issue = {33},
pages = {1878--1892.e5},
abstract = {F. nucleatum is a Gram-negative bacteria that causes oral infections and is linked to colorectal cancer. Pathogenicity relies on a type of β-barrel outer membrane protein (OMP) called an autotransporter. The biogenesis of OMPs is typically mediated by the barrel assembly machinery (BAM) complex. In this study, we investigate the evolution, composition, and structure of the OMP biogenesis machinery in F. nucleatum. Our bioinformatics and proteomics analyses indicate that OMP biogenesis in F. nucleatum is mediated solely by the core component BamA. The structure of FnBamA highlights distinct features, including four POTRA domains and a C-terminal 16-stranded β-barrel domain observed as an inverted dimer. FnBamA represents the original composition of the assembly machinery, and a duplication event that resulted in BamA and TamA occurred after the split of other lineages, including the Proteobacteria, from the Fusobacteria. FnBamA, therefore, likely serves a singular role in the biogenesis of all OMPs.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
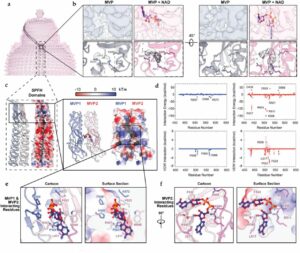
Lodwick J E; Shen R; Erramilli S; Xie Y; Roganowicz K; Kossiakoff A A; Zhao M
Structural Insights into the Roles of PARP4 and NAD in the Human Vault Cage Journal Article
In: Nature Communications, iss. 16, no. 6724, 2025, ISSN: 2692-8205.
@article{pmid38979142,
title = {Structural Insights into the Roles of PARP4 and NAD in the Human Vault Cage},
author = {Jane E Lodwick and Rong Shen and Satchal Erramilli and Yuan Xie and Karolina Roganowicz and Anthony A Kossiakoff and Minglei Zhao},
doi = {10.1038/s41467-025-61981-x},
issn = {2692-8205},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-07-21},
urldate = {2024-06-01},
journal = {Nature Communications},
number = {6724},
issue = {16},
abstract = {Vault is a massive ribonucleoprotein complex found across Eukaryota. The major vault protein (MVP) oligomerizes into an ovular cage, which contains several minor vault components (MVCs) and is thought to transport transiently bound "cargo" molecules. Vertebrate vaults house a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (known as PARP4 in humans), which is the only MVC with known enzymatic activity. Despite being discovered decades ago, the molecular basis for PARP4's interaction with MVP remains unclear. In this study, we determined the structure of the human vault cage in complex with PARP4 and its enzymatic substrate NAD . The structures reveal atomic-level details of the protein-binding interface, as well as unexpected NAD -binding pockets within the interior of the vault cage. In addition, proteomics data show that human vaults purified from wild-type and PARP4-depleted cells interact with distinct subsets of proteins. Our results thereby support a model in which PARP4's specific incorporation into the vault cage helps to regulate vault's selection of cargo and its subcellular localization. Further, PARP4's proximity to MVP's NAD -binding sites could support its enzymatic function within the vault.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
